A Strategic Imperative for Operations and Engineering Personnel
Indonesia, a cornerstone of Southeast Asia's energy landscape, stands at a critical juncture. The nation's oil and gas sector, vital to its economic stability, faces a dual challenge: meeting the escalating energy demands of a rapidly developing economy while simultaneously addressing the global imperative for a transition to more sustainable energy sources.
This white paper examines the complexities of Indonesia's energy transition, the hidden challenges within its energy infrastructure, and the transformative power of digitalisation in navigating this evolving landscape.

Visualising the Energy Transition in Indonesia
Indonesia's energy transition is not a simple switch from fossil fuels to renewables. It's a multifaceted challenge, demanding a carefully orchestrated strategy that balances economic growth, energy security, and environmental sustainability. The nation's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, as outlined in its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) under the Paris Agreement, necessitates a significant shift in its energy mix.
Key aspects of this transition include:
- Increased Renewable Energy Integration: Harnessing Indonesia's vast potential for solar, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy. For instance, Indonesia has significant geothermal potential, holding 40% of the world's geothermal resources.
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: Reducing energy intensity across industries and promoting energy conservation.
- Decarbonisation of Fossil Fuels: Implementing technologies like carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS) to mitigate emissions from existing oil and gas operations. BP is involved in a significant CCUS project in Tangguh, demonstrating a commitment to decarbonising gas production.
- Development of Green Technologies: Investing in hydrogen, biofuels, and other alternative energy sources.
This transition requires a long-term vision, strategic planning, and substantial investment. It also necessitates a deep understanding of the current energy landscape and the challenges that lie ahead. According to the Handbook of Energy & Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2023, the primary energy mix is still dominated by coal (39.69%), followed by petroleum (29.91%), natural gas (17.11%), and renewables (13.29%) [ESDM]. These statistics highlight the dominance of fossil fuels and the need for a greater shift towards renewables.
We invite you to:
- Join our upcoming webinar to delve deeper into the specific digital solutions that can transform your operations and drive your organisation's success in the evolving energy landscape. Register now.
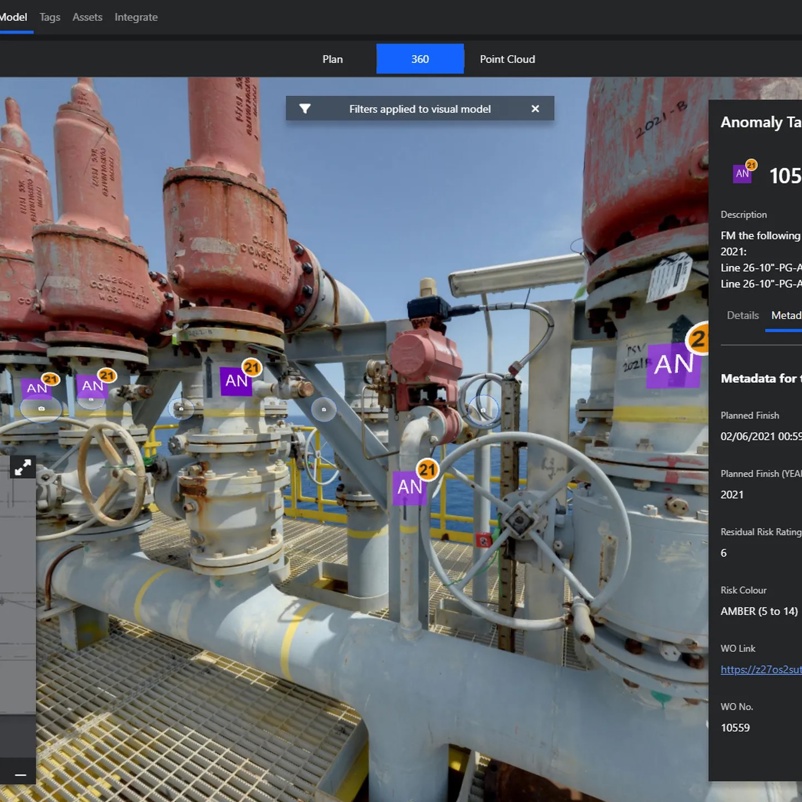
- Engage with our Sales Team to explore how a Proof of Concept (POC) using our R2S digital twin platform —already proven in the region. In Southeast Asia, R2S supported operational teams at the Tangguh gas field, helping reduce costs by up to $3.5 million while improving visibility and planning in hazardous environments. R2S, a leading visual asset management tool, empowers teams overseeing critical infrastructure by enhancing access to asset information in hazardous environments. With R2S, you can embark on a journey of digital transformation, emphasising change management and value creation. Let us partner with you on your journey to digital transformation.
References
- Handbook of Energy & Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2023 - ESDM
- Indonesia Energy Transition Outlook 2025 - IESR

This white paper examines the complexities of Indonesia’s energy transition, the hidden challenges within its energy infrastructure, and the transformative power of digitalisation in navigating this evolving landscape.




 Read James Fisher and Sons plc's latest Annual Report
Read James Fisher and Sons plc's latest Annual Report